13. Statistics, Tests and Measurements (Ch2)
13.1 Descriptive and Inferential Statistics Samples, populations, norms
- Statistics
- collection, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of numeric data
- Samples
- representative subset of larger population
- random sample
- Populations
- group of people looking to study
- Norms
- identifying normal behavior of group to compare to
- standardizing
- Descriptive Statistics
- used for correlational and experimental designs
- measurements of behavior from sample
- Mean
- average
- Mode
- most commonly occurring score
- Median
- middle score, separates lower and upper halves of scores
- Standard Deviation
- statistical measure of how much scores in a sample vary around the mean
- higher SD = more variability (more spread)
- lower SD = less variability (less spread)
- Normal Distribution
- bell curve showing symmetrical alignment of two variables (e.g Intelligence)
- Inferential Statistics
- inferences about population based on characteristics of sample
- statistical significance
- not likely to have happened by chance
- significant equals 5% of the time or less
13.2 Reliability and Validity
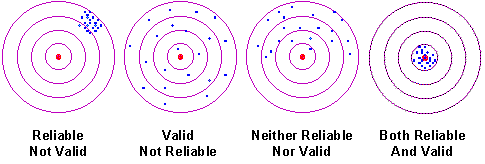
Reliability
- stability and consistency of scores
- does not need to be valid to be reliable
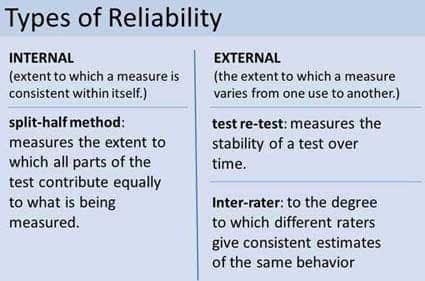
Types of Reliability
- test-retest reliability
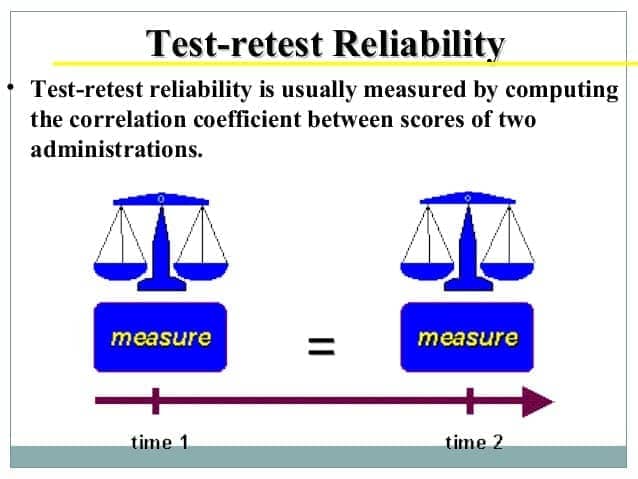
- internal consistency
- How well does a test correlate with itself
- split-half reliability
- Cronbach’s alpha: avg correlation for every way a test can be split in half
Validity
- how well a test measures what it is supposed to measure
- must be reliable to be valid
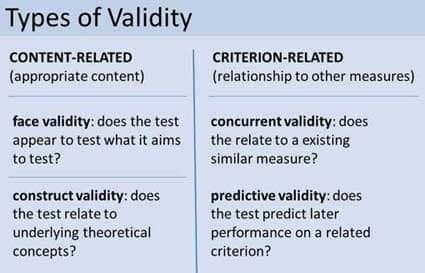
Types of validity
- face/content validity
- whether a test looks as though it is measuring what it is supposed to measure
- predictive validity
- how well scores on the test predict the actual behavior of the type that the test is supposed to measure
- construct validity
- whether the scores on a questionnaire are related in expected ways, either positively or negatively, to scores on other questionnaires that are proposing to measure the same thing.
- whether the scores on a questionnaire are related in expected ways, either positively or negatively, to scores on other questionnaires that are proposing to measure the same thing.
- face/content validity
standardizing measures
13.3 Types of Tests
- Tests used to rule out chance
- t-test: computed for two means to see if they come from same population (e.g., of two groups or variables)
- ANOVA: analysis of variance
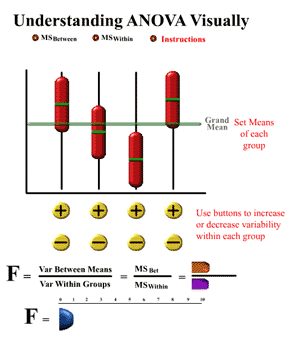
- Pearson correlation coefficient (-1.0 to +1.0)
13.4 Measurement of Intelligence
Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale
- first IQ test
- still widely used today
- norming and standardization
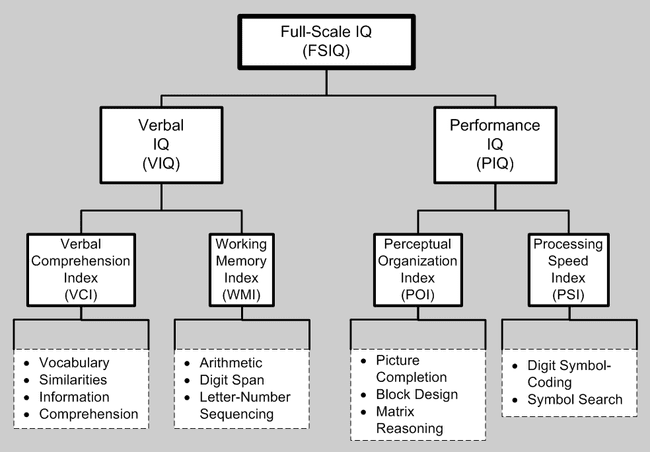
Wechsler Intelligence Tests
- WAIS- IV: Adult
- WISC-V: Children
- WPPSI-IV: Pre-school and primary school
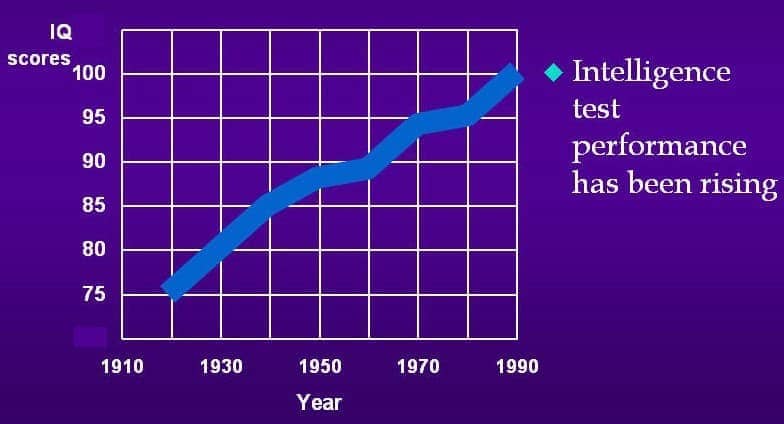
Flynn effect
- each generation, higher IQ
Quiz
- Which of the following is a measure of central tendency that can be easily distorted by unusually high or low scores?
- (A) Mean
- (B) Mode
- (C) Median
- (D) Range
- (E) Standard deviation
- Which of the following statistics indicates the distribution with the greatest variability?
- A variance of 30.6
- (B) A standard deviation of 11.2
- (C) A range of 6
- (D) A mean of 61.5
- (E) A median of 38
- Which of the following is a true statement about the relationship between test validity and test reliability?
- (A) A test can be reliable without being valid.
- (B) A test that has high content validity will have high reliability.
- (C) A test that has low content validity will have low reliability.
- (D) The higher the test’s validity, the lower its reliability will be.
- (E) The validity of a test always exceeds its reliability.
- If the null hypothesis is rejected, a researcher can conclude that the
- (A) treatment effect was significant
- (B) theory must be modified, a new hypothesis formed, and the experimental procedure revised
- (C) theory does not need modification, but the hypothesis and the experimental procedure need revision
- (D) theory and hypothesis do not need modification, but the experimental procedure needs revision
- (E) hypothesis is false
- In order to illustrate how often a particular score occurs in a given data set, researchers use
- (A) inferential techniques
- (B) cognitive mapping
- (C) cluster analysis
- (D) the median
- (E) a frequency distribution